引言
路由即根据不同的路径渲染不同的组件 实现方式有两种:
HashRouter: 利用hash实现路由的切换
BrowserRouter:利用h5 api 实现路由的切换
自己手写实现react-router,彻底掌握react-router原理,我将以这样的顺序进行。
- 路由的两种实现方式
- 实现react-router-dom
- 实现Router和Route
- 实现hashHistory
- 实现browserHistory
- 正则表达式的应用
- 实现matchPath
- 实现Switch
- 实现Redirect、Link
- 实现嵌套路由
- 受保护路由
- 实现NavLink
- 实现WithRouter、Prompt
- 实现react-router(路由)中的hooks
props路由参数: history:历史对象 location: 路径对象 match: 匹配参数
hashRouter的实现方式
function createHashHistory() {
let action;
const listeners = [];
const historyStack = [];//历史栈
let historyIndex = -1;
let state;
function listen(listener){
listeners.push(listener);
return () => {
const index = listeners.indexOf(listener);
listeners.splice(index, 1);
}
}
const hashChange = () => {
let pathname = window.location.hash.slice(1);
Object.assign(history, { action, location: { pathanme, state }})
}
if(!action || action === 'PUSH') {
historyStack[++historyIndex] = history.location;
}else if(action === 'REPLACE'){
historyStack[historyIndex] = history.location;
}
listeners.forEach(listener => listener(history.location));
}
window.addEventListener('hashChange', hashChange);
function push(pathname, nextState) {
/* history.push('user', {name: 'tom'}) ; history.push({ pathname: '/user', state: {name: "用户管理"} })*/
action = 'PUSH';
if(typeof pathname === 'object') {
state = pathname.state;
pathname = pathname.pathname;
}else {
state = nextState;
}
window.location.hash = pathname;
}
function replace(pathname, nextState) {
if(typeof pathname === 'object') {
pathname = pathname.pathname;
state = pathname.state;
}else {
state = nextState;
}
window.location.hash = pathname;
}
/* go通过历史栈实现 */
function go(n) {
action = 'POP';
historyIndex += n;
const nextLocation = historyStack[historyIndex];
state = nextLocation.state;
window.location.hash = nextLocation.pathname;
}
function goBack(-1) {
go(-1);
}
function goForward() {
go(1);
}
/* hashHistory中的history没有兼容性问题 */
const history = {
action: 'POP',
location: { pathname: "/", state: undefined },
go,
goBack,
goForward,
push,
replace,
listen
}
action = 'PUSH';
if(window.location.hash) {
hashChange();
}else {
window.location.hash = '/';
}
return history;
browserHistory的实现方式
利用H5 API实现路由的切换,HTML5规范给我们提供了一个history接口,HISTORY给我们提供了两个方法一个事件: history.pushState()和history.replaceState()、window.onpopstate。
history.pushState(stateObject, title, url),包括三个参数
第一个参数用于存储该url对应的状态对象,该对象可在onpopstate事件中获取,也可在history对象中获取
第二个参数是标题,目前浏览器并未实现
第三个参数则是设定的url
pushState函数向浏览器的历史堆栈压入一个url为设定值的记录,并改变历史堆栈的当前指针至栈顶
history.replaceState(stateObject, title, url):
该接口与pushState参数相同,含义也相同
唯一的区别在于replaceState是替换浏览器历史堆栈的当前历史记录为设定的url
需要注意的是replaceState不会改动浏览器历史堆栈的当前指针
history.onpopstate,该事件是window的属性
该事件会在调用浏览器的前进、后退以及执行history.forward、history.back、和history.go触发,因为这些操作有一个共性,即修改了历史堆栈的当前指针
在不改变document的前提下,一旦当前指针改变则会触发onpopstate事件
function createBrowserHistory() {
const globalHistory = window.history;
const listeners = [];
let action, state, message;
function go(n) {
globalHistory.go(n);
}
function goForward() {
go(1);
}
function goBack(n) {
go(-1);
}
function listen(listener) {
listeners.push(listener);
return () => {
let index = listeners.indexOf(listener);
listeners.splice(index, 1);
}
}
function setState(newState) {
Object.assign(history, newState);
listeners.forEach(listener => listener(history.location));
}
function push(pathname, nextState) {
action = 'PUSH';
if(typeof pathname === 'object') {
state = pathname.state;
pathname = pathname.pathname;
}else { state = nextState }
if(messgage) {
let showMessage = message({ pathname });
let allow = window.confirm(showMessage);
if(!allow) return;
}
globalHistory.pushState(state, null, pathname);
let location = { state, pathname };
setState({ action, location });
}
/* 当回退或者前进的时候执行该函数,浏览器自带的,默认支持 */
window.onpopstate = (event) => {
setState({ action: 'POP', location: { pathname: window.location.pathname, state: globalHistory.state }})
}
function block(newMessage) {
message = newMessage;
return () => message = null;
}
const history = {
action: 'POP';
location: { pathname: window.location.pathname, state: globalHistory.state },
go,
goForward,
goBack,
push,
listen,
block
}
return history;
}
实现matchPath
import pathToRegexp from 'path-to-regexp';
const cache = {};
function compilePath(path, options = {}) {
let cacheKey = path + JSON.stringify(options);
if (cache[cacheKey]) return cache[cacheKey];
const keys = [];//处理路径参数
const regexp = pathToRegexp(path, keys, options);
let result = { keys, regexp };
cache[cacheKey] = result;
return { keys, regexp };
}
/*
pathname: 浏览器当前真实的路径名
options: Route组件的props path Component exact
path Route的路径
exact 是否精确匹配
strict 是否严格匹配
sensitive 是否大小写敏感
*/
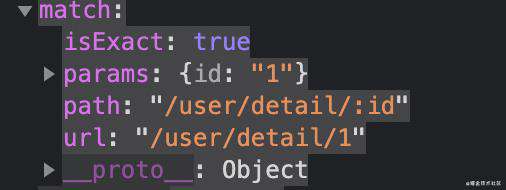
/* 根据路径匹配到match */
function matchPath(pathname, options = {}) {
let { path = '/', exact = false, strict = false, sentive = false } = options;
let { keys, regexp } = compilePath(path, { end: exact, strict, sentive });
const match = regexp.exec(pathname);
if (!match) return null;
const [url, ...values] = match;
const isExact = pathname === url;
/* 要求精确但是并不精确 */
if (exact && !isExact) return null;
return {
path,//来自Route里的path路径
url,//来自浏览器地址中的url
isExact,//是否精确匹配
params: keys.reduce((memo, key, index) => {
memo[key.name] = values[index];
return memo;
}, {})
}
}
export default matchPath;
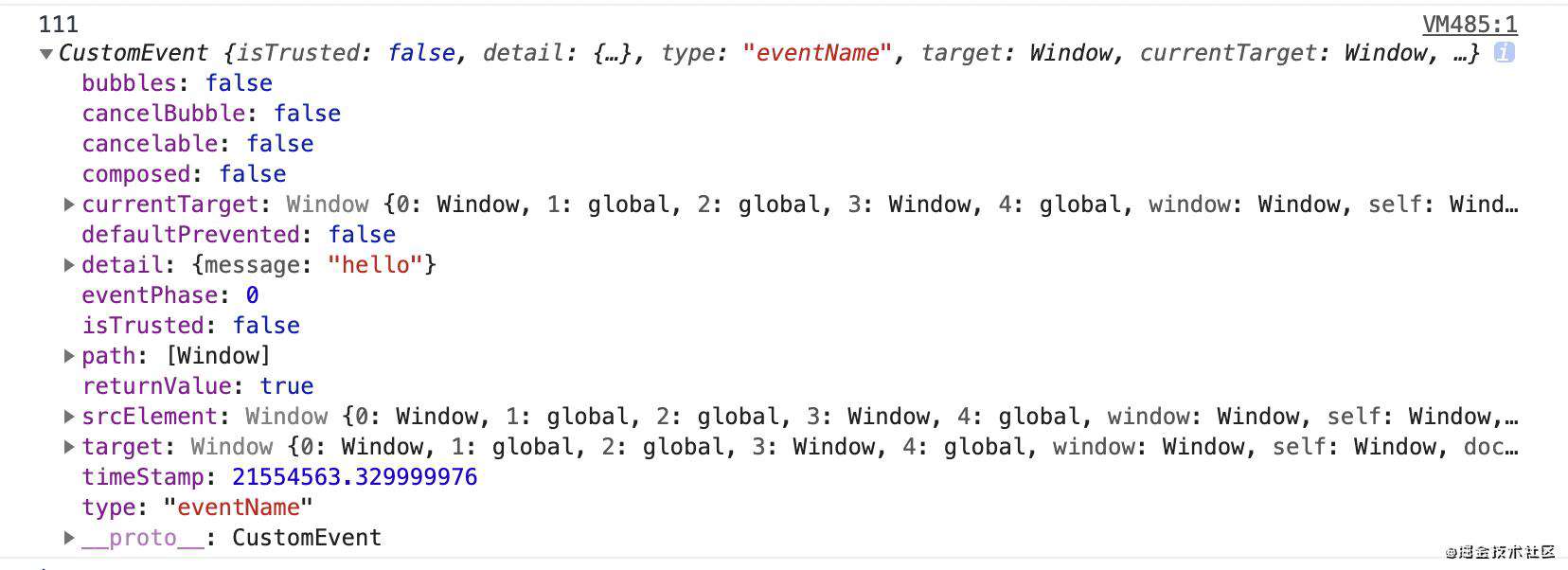
- 自定义event事件:使用customEvent构造函数
window.addEventListener('eventName', (e) => {
console.log('111', e);
})
let event = new CustomEvent('eventName', {
detail: {
message: 'Hello World'
}
})
window.dispatchEvent(event);
正则表达式的使用
- path-to-regext 把路径转成一个正则,跟真实的路径做匹配
正则表达式可视化工具: jex.im/regulex/#!f…
- 嵌套路由不需要在源码中有额外的代码,Route已经有支持了
剩下的内容见: github.com/China-forre…
常见问题FAQ
- 免费下载或者VIP会员专享资源能否直接商用?
- 本站所有资源版权均属于原作者所有,这里所提供资源均只能用于参考学习用,请勿直接商用。若由于商用引起版权纠纷,一切责任均由使用者承担。更多说明请参考 VIP介绍。
- 提示下载完但解压或打开不了?
- 找不到素材资源介绍文章里的示例图片?
- 模板不会安装或需要功能定制以及二次开发?






发表评论
还没有评论,快来抢沙发吧!